

- CALCULATE PI OF AMINO ACID IN THE MIDDLE OF A POLYPEPTIDE CODE
- CALCULATE PI OF AMINO ACID IN THE MIDDLE OF A POLYPEPTIDE FREE
Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. The three-dimensional structures of both proteins were first determined by X-ray diffraction analysis Perutz and Kendrew shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for these discoveries. The first protein structures to be solved were hemoglobin and myoglobin, by Max Perutz and Sir John Cowdery Kendrew, respectively, in 1958. Sumner showed that the enzyme urease was in fact a protein.The first protein to be sequenced was insulin, by Frederick Sanger, who won the Nobel Prize for this achievement in 1958. Early nutritional scientists such as the German Carl von Voit believed that protein was the most important nutrient for maintaining the structure of the body, because it was generally believed that "flesh makes flesh." The central role of proteins as enzymes in living organisms was however not fully appreciated until 1926, when James B. Proteins were first described by the Dutch chemist Gerhardus Johannes Mulder and named by the Swedish chemist Jöns Jakob Berzelius in 1838.

CALCULATE PI OF AMINO ACID IN THE MIDDLE OF A POLYPEPTIDE FREE
Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Not all proteins requiring a folding process in order to function, as some function in an unfolded state. Thus, the structure of a protein serves as a medium through which to regulate either the function of a protein or activity of an enzyme. This conformational change is often associated with a signaling event. Other proteins undergo large rearrangements from one conformation to another. Some proteins fold into a highly rigid structure with small fluctuations and are therefore considered to be single structure. The extent to which proteins fold into a defined structure varies widely.
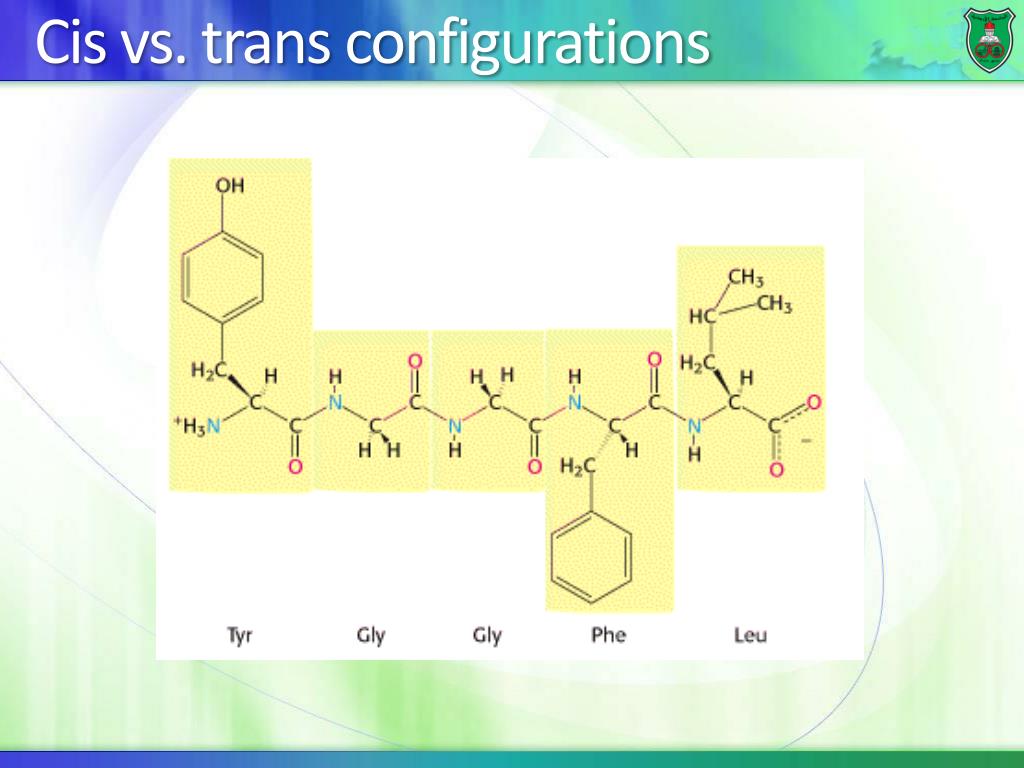
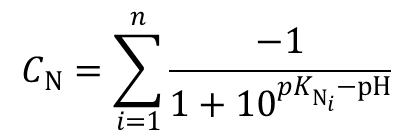
One of the most distinguishing features of polypeptides is their ability to fold into a globular state, or "structure". Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable complexes. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by post-translational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins.
CALCULATE PI OF AMINO ACID IN THE MIDDLE OF A POLYPEPTIDE CODE
In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine-and in certain archaea-pyrrolysine. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acid residues. They are particularly important in biochemistry, where the term usually refers to alpha-amino acids.Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group(NH 2), a carboxylic acid group(R-C=O-OH) and a side-chain( usually denoted as R) that varies between different amino acids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
